4. Let’s learn about welding!~Projection Welding~
2024/11/15
Previously, Kyappa-kun learned about the combination of parts used in spot welding. This time, let’s learn
about projection welding.
[What is Projection Welding?]
Projection welding is a type of resistance welding where a protrusion is created on a nut or bolt. The current and pressure are concentrated between this protrusion (called a projection) and the base material, using resistive heat to create a molten, pressure-bonded weld.
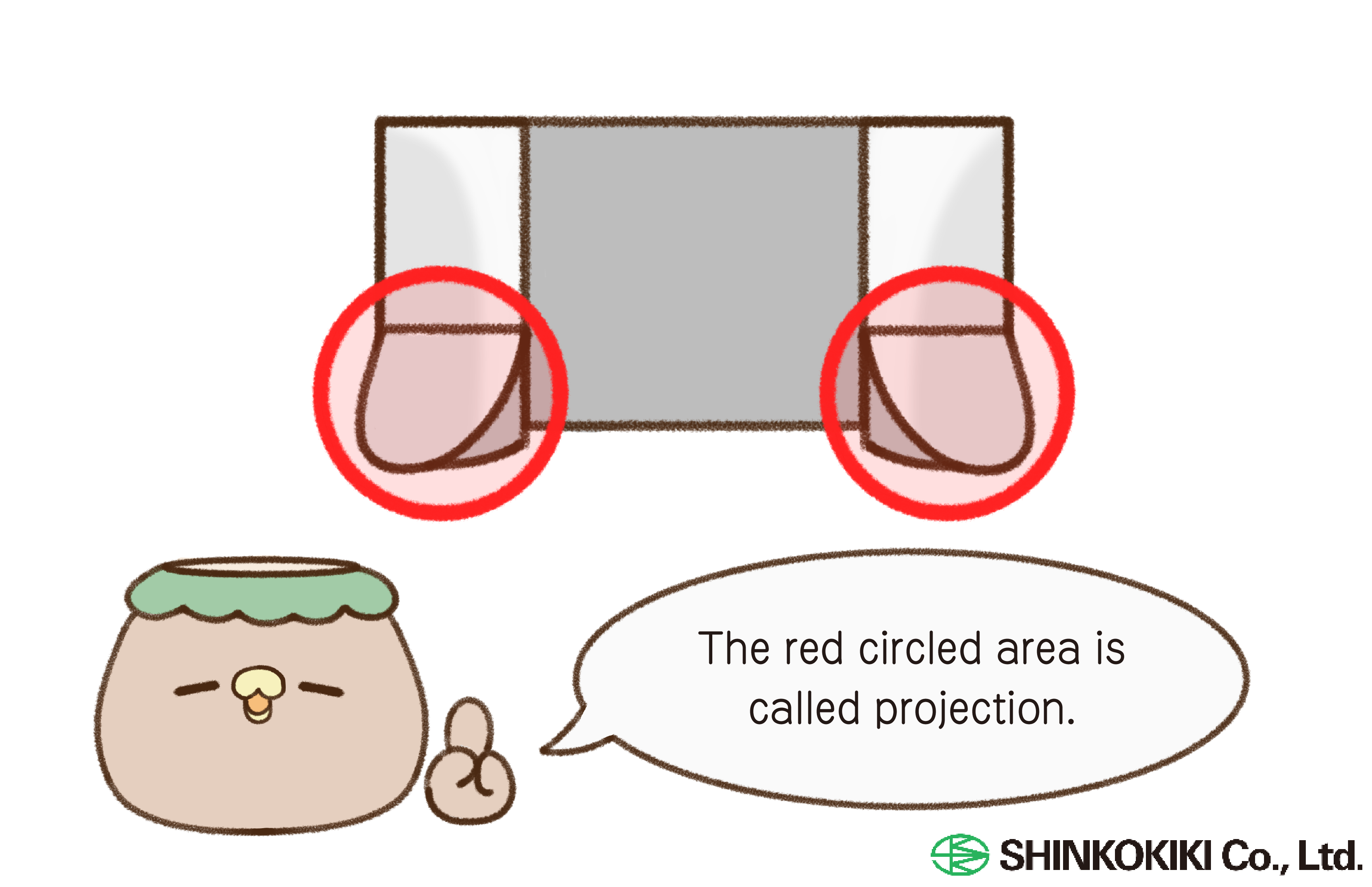
[Names and Combinations of Each Part (Nut Welding Version)]
In nut welding, the lower assembly consists of three main components: the lower electrode, guide pin, and lower electrode holder. The upper assembly uses parts such as our upper electrode products.
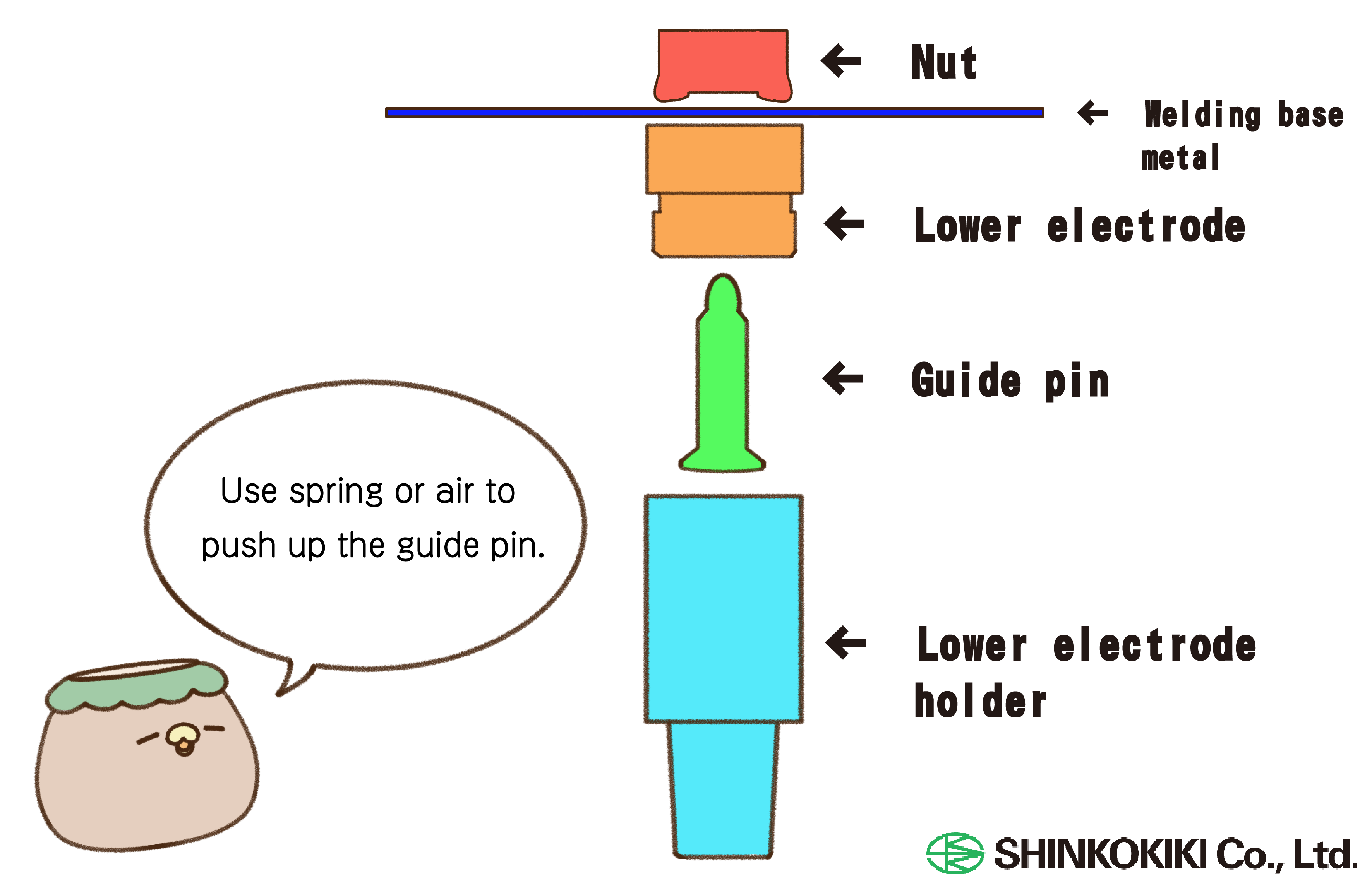
[What is a Guide Pin?]
A guide pin, as the name suggests, serves as a guiding tool during welding and is used specifically when welding nuts.
In projection welding for nuts, the workpiece has a hole to allow for bolt assembly later on. Ideally, the nut should be centered over this hole for proper alignment. This is where the guide pin becomes essential.
For example, with an M6 nut, a φ7.0 hole might be drilled in the workpiece. A guide pin with a body diameter of φ6.8 is then selected. This creates a gap of -0.1 mm on each side, ensuring near-perfect centering. By guiding the nut in this way, it is welded precisely in the center of the hole, preventing any issues during later bolt assembly.
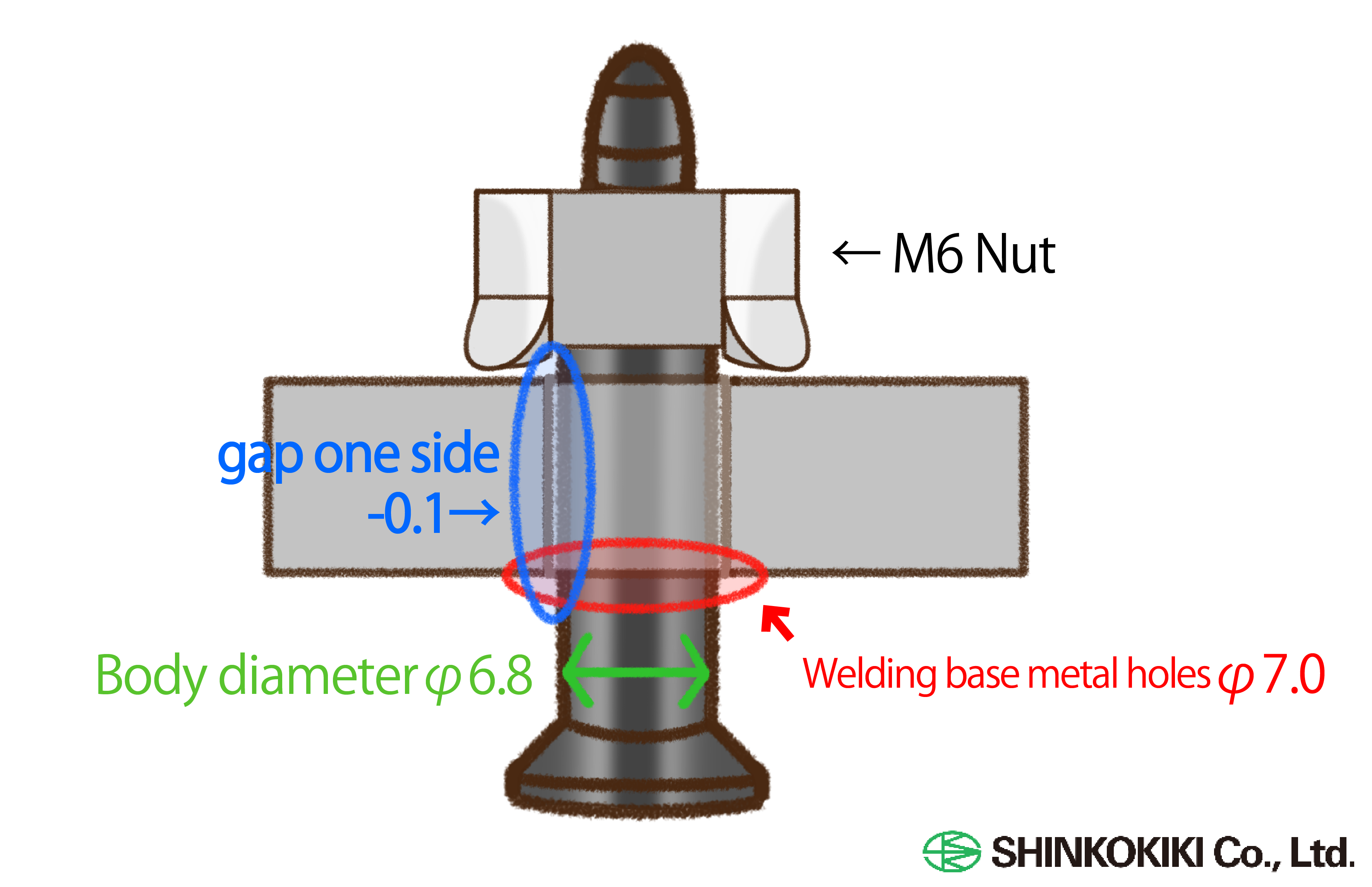
Since the guide pin’s purpose is to align the nut, using a conductive material would cause the pin and nut to fuse together. To prevent this, the guide pin must be insulated.
Our guide pins are available in two materials: KCF and ceramics. KCF is a specially treated stainless steel with an electrically insulating coating, while ceramics is a non-metallic electrical insulator. Let’s explore the unique characteristics of each—KCF guide pins and ceramic guide pins.
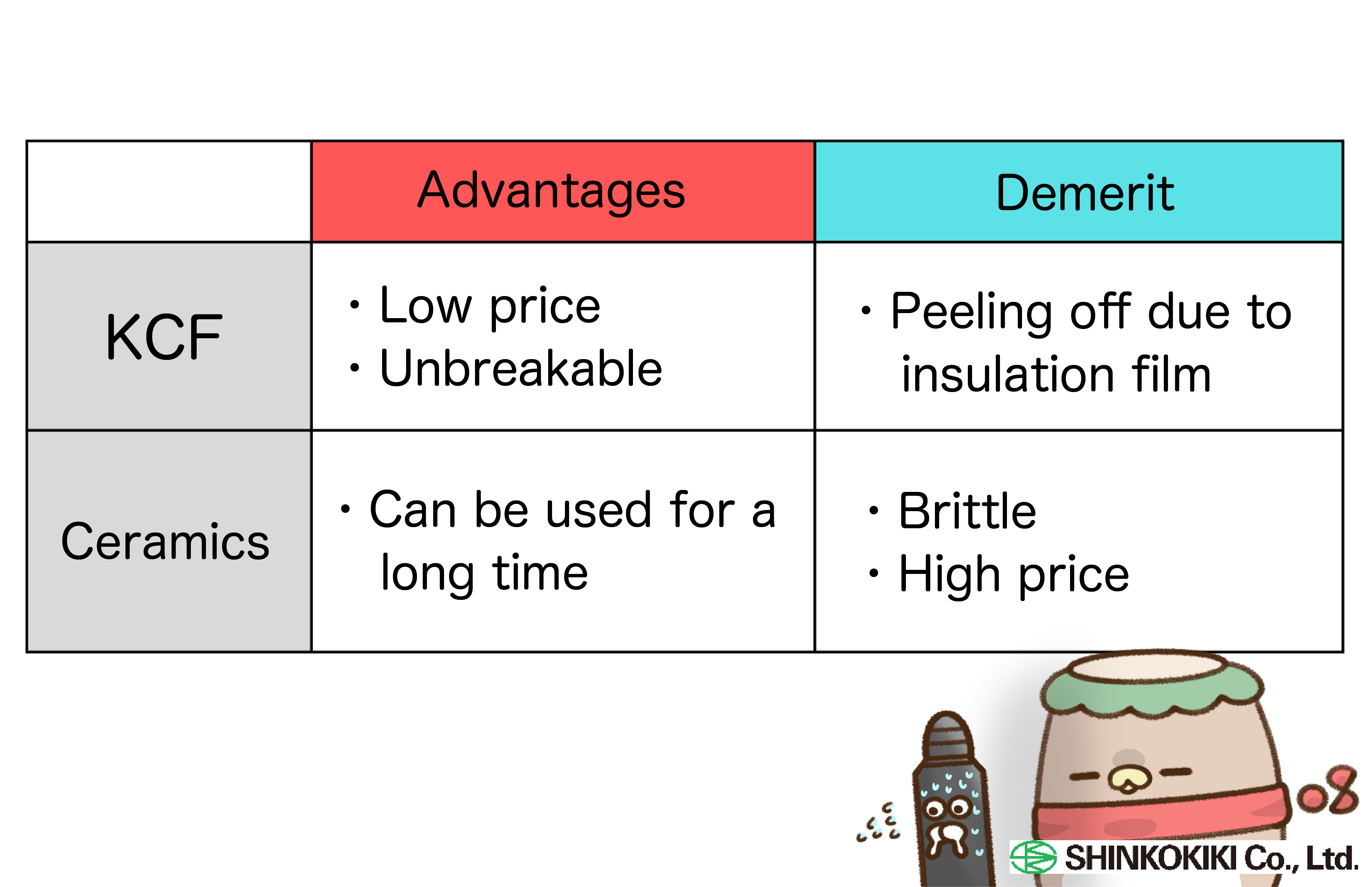
The choice between KCF and ceramic guide pins depends on factors such as nut type, base material size, whether the process is automated (robotic) or manual, as well as considerations for work efficiency and cost.
That’s all for this time.
See you in the next column!
